Get Started
Before reading this guide, we assume you either have a Kubernetes cluster, or a local Kubernetes dev environment, e.g MiniKube.
It is also assumed that kubectl is on your path and properly configured.
Follow this guide on how to setup a local Kubernetes cluster using docker-desktop.
Install
The easiest way to get started is to use our Helm Charts to deploy YuniKorn on an existing Kubernetes cluster. It is recommended to use Helm 3 or later versions.
helm repo add yunikorn https://apache.github.io/incubator-yunikorn-release
helm repo update
kubectl create namespace yunikorn
helm install yunikorn yunikorn/yunikorn --namespace yunikorn
By default, the helm chart will install the scheduler, web-server and the admission-controller in the cluster.
When admission-controller is installed, it simply routes all traffic to YuniKorn. That means the resource scheduling
is delegated to YuniKorn. You can disable it by setting embedAdmissionController flag to false during the helm install.
Further configuration options for installing YuniKorn via Helm are available in the YuniKorn Helm hub page.
If you don't want to use helm charts, you can find our step-by-step tutorial here.
Uninstall
Run the following command to uninstall YuniKorn:
helm uninstall yunikorn --namespace yunikorn
Access the Web UI
When the scheduler is deployed, the web UI is also deployed in a container. Port forwarding for the web interface on the standard port can be turned on via:
kubectl port-forward svc/yunikorn-service 9889:9889 -n yunikorn
9889 is the default port for web UI.
Once this is done, web UI will be available at: http://localhost:9889.
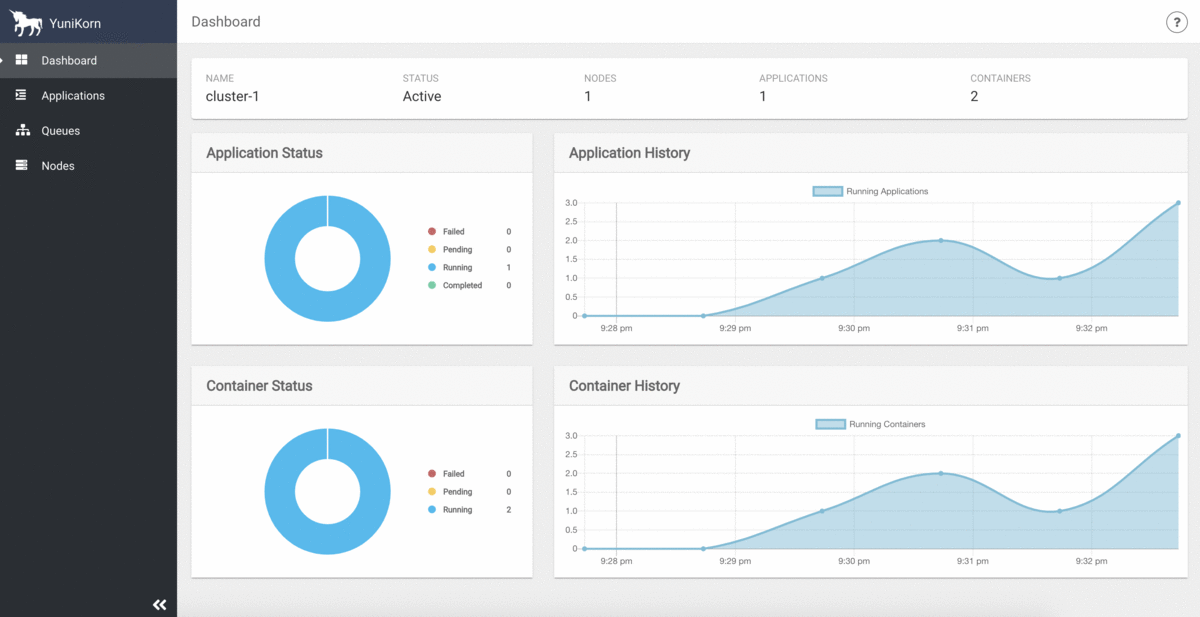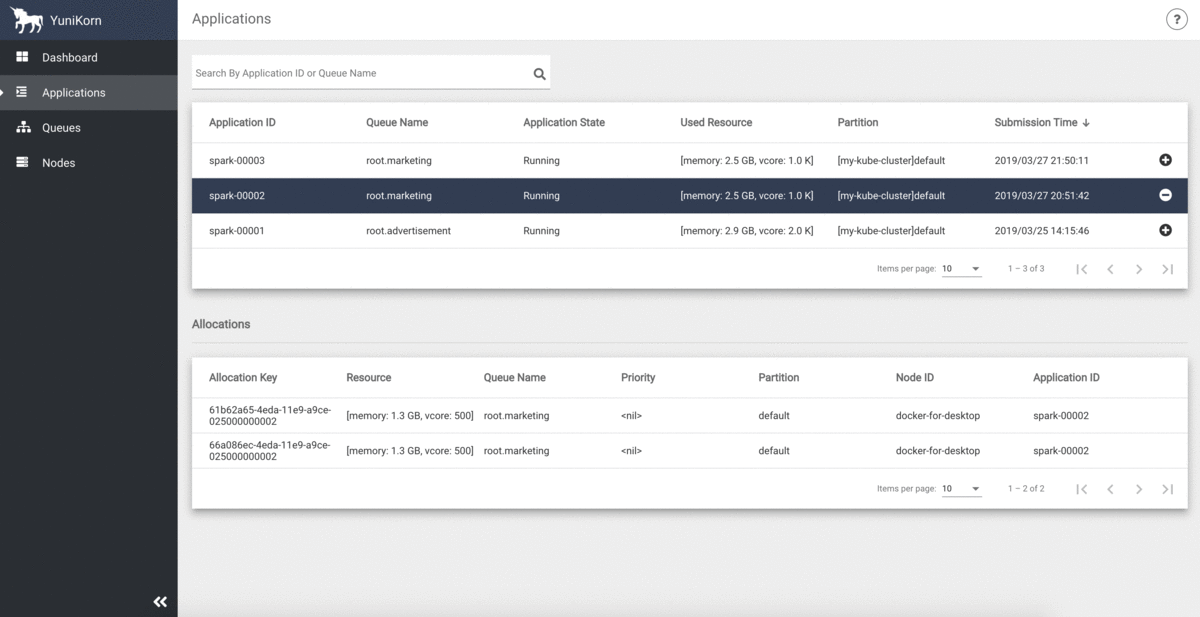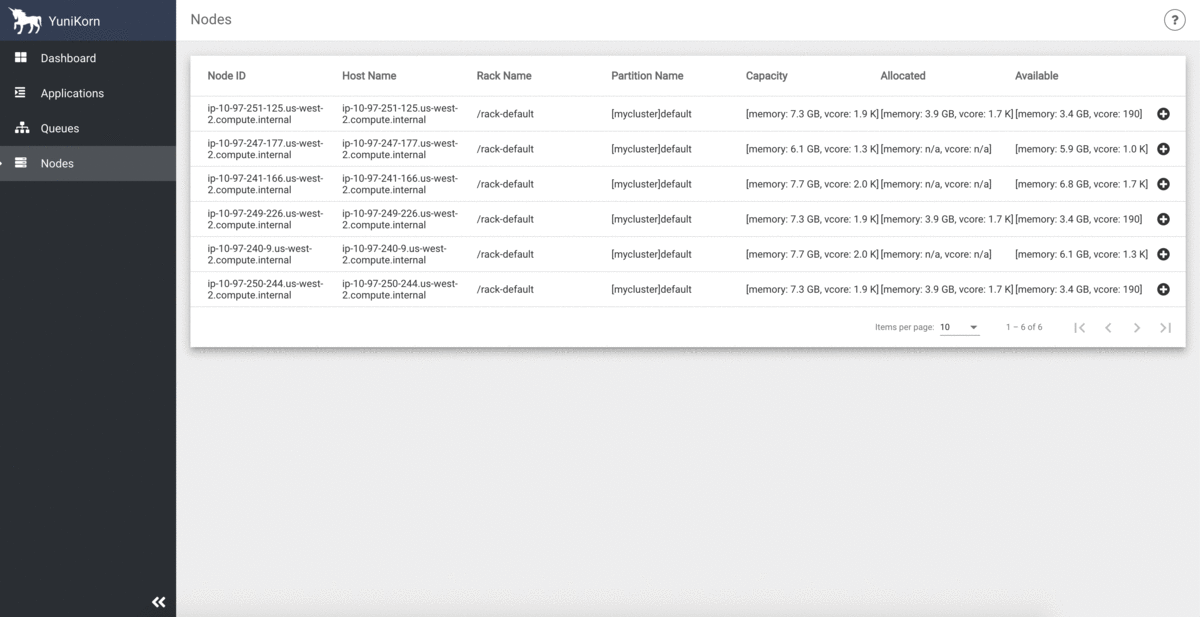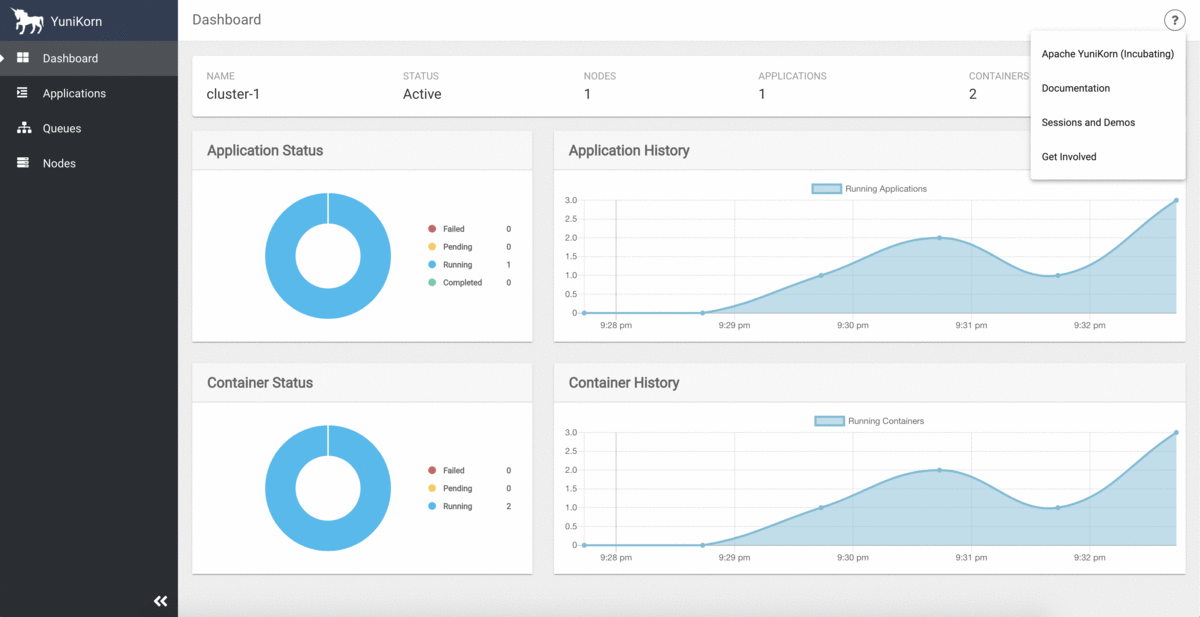
YuniKorn UI provides a centralised view for cluster resource capacity, utilization, and all application info.